Jupiter Atmospheric Probe
From Spacefaring
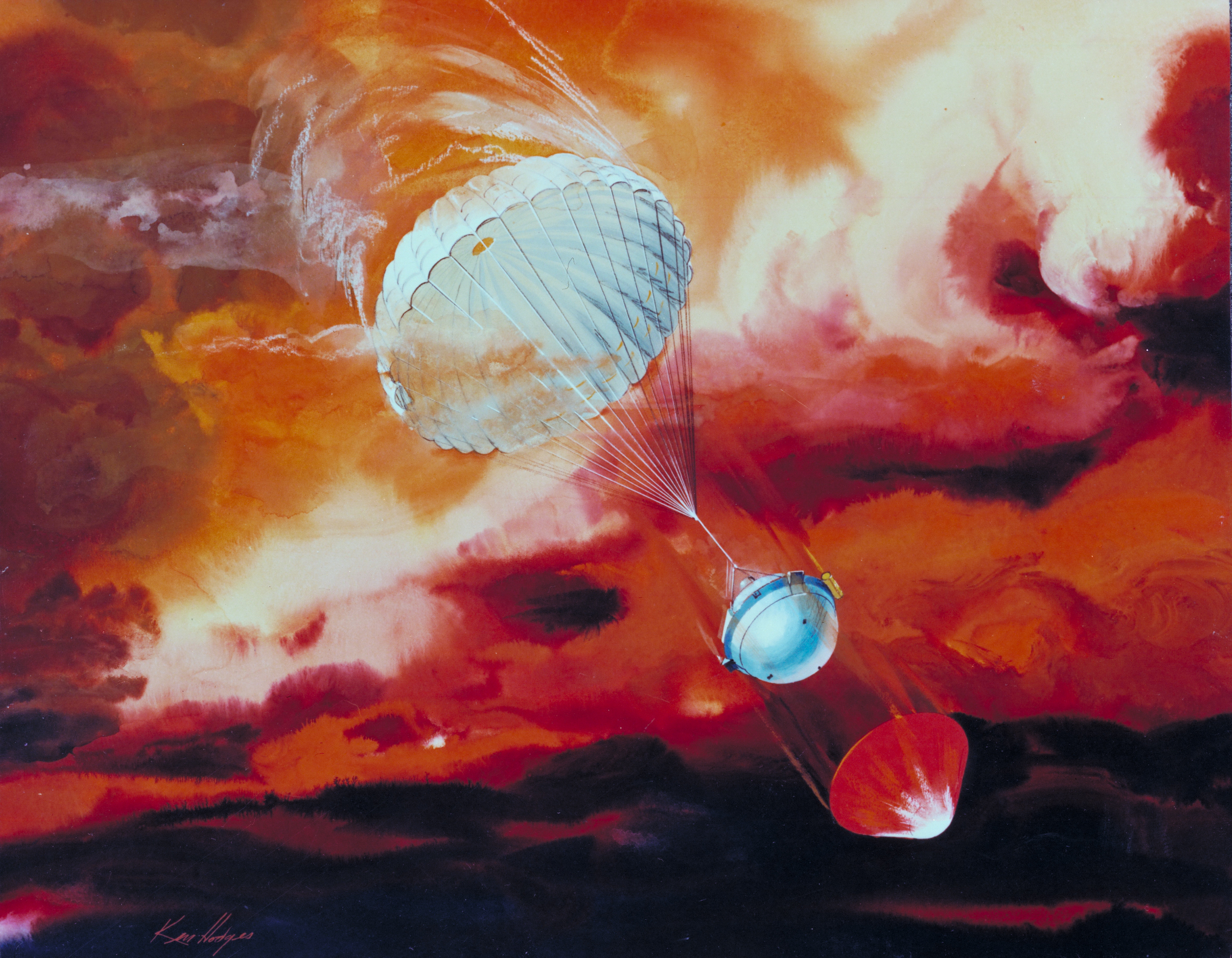
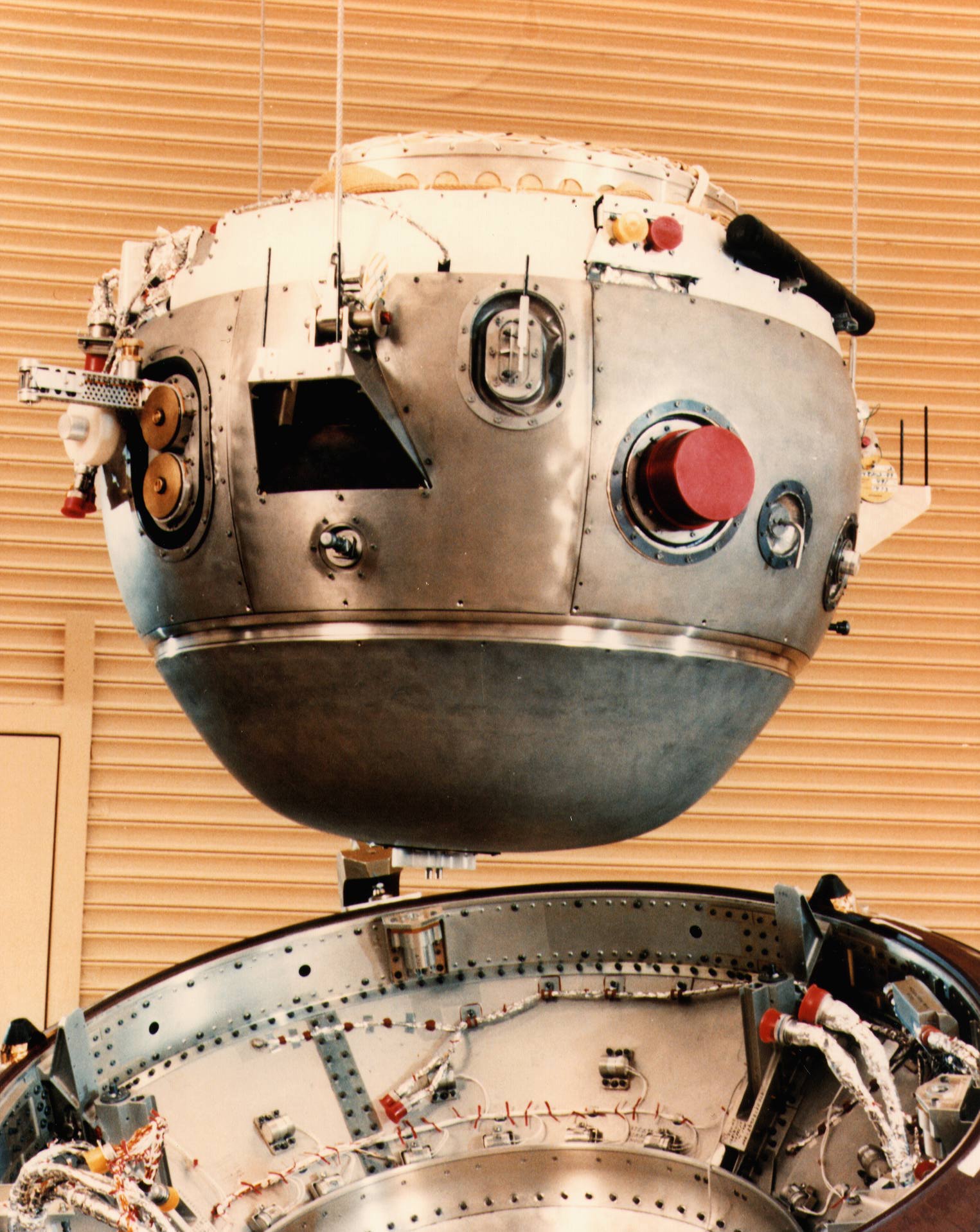
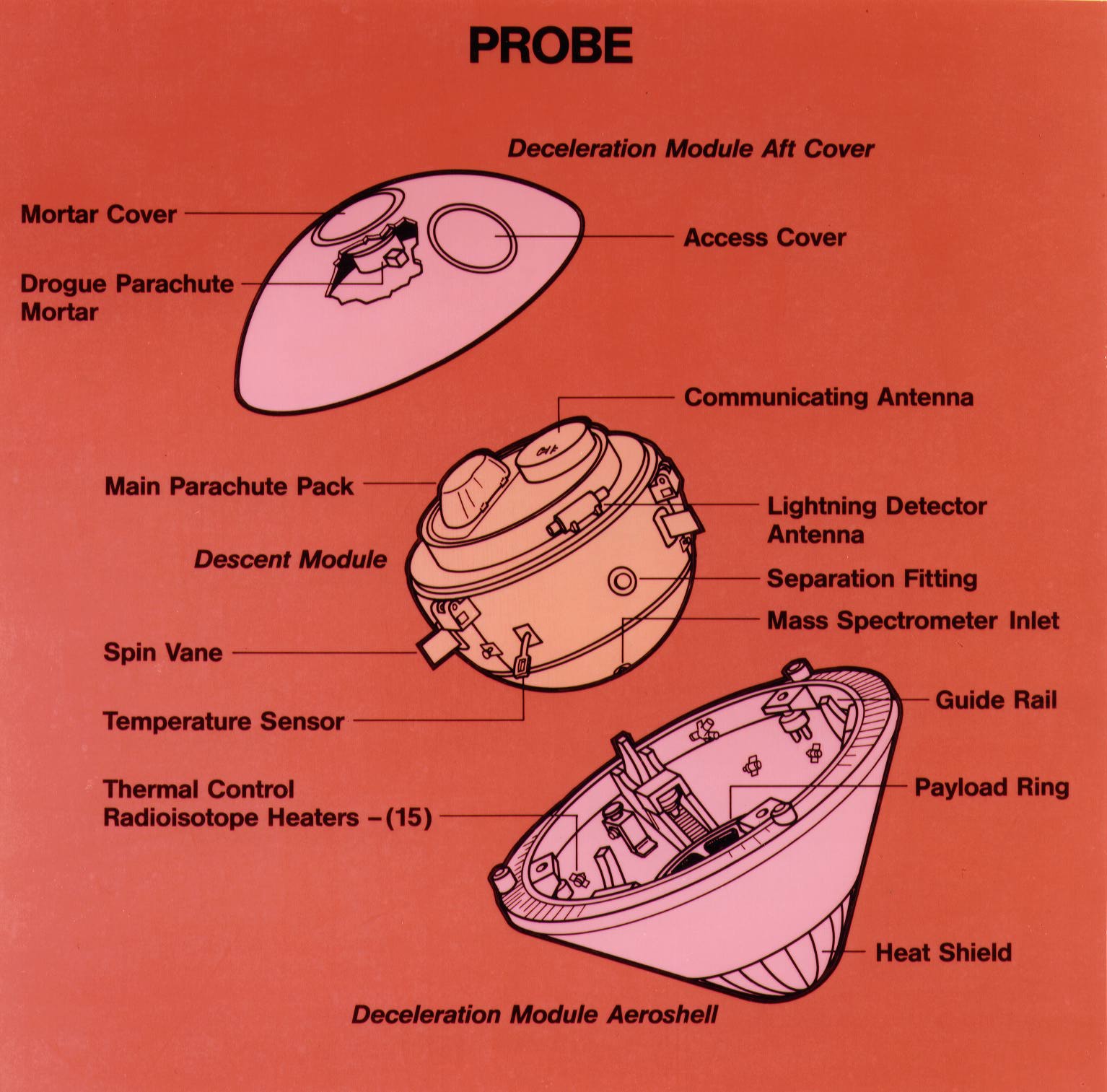
Galileo was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by Space Shuttle Atlantis, during STS-34. Galileo arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet.
Wikimedia, Wikidata
Galileo Atmospheric Probe; Galileo Descent Module; Galileo Entry Probe; Galileo Jupiter Atmospheric Probe; Galileo Probe; JEP; JOP; Jupiter Entry Probe; Jupiter Orbiter Probe
-
Location: 6.5, -4.4, KML, Cluster Map, Maps,
1 places
{"selectable":false,"showCurrentTime":false,"width":"100%","zoomMin":100000000000}
| Type | Subtype | Date | Description | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | space object | Jupiter Atmospheric Probe | former entity, reentry vehicle, space probe, | Wikidata | |
| incident | incident | [[1]] | Wikidata | ||
| commons | image | Galileo probe | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Parachute deployment | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Descent Module | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo Probe | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo Probe diagram | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo Probe (4995921381) | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo probe heat loads | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo Probe - AC81-0174 | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo Jupiter Atmospheric Probe in a spacecraft processing room (AC84-0228-3) | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Galileo Probe Descent module and deceleration module aeroshell (AC84-0228-05) | Commons | ||